May/June 2018
Communities: Education
MIT Study: Dramatic Shifts Anticipated In Engineering Education Leadership
Characteristics of ‘Emerging Leader’ Institutions
According to the MIT-commissioned study, emerging leader institutions included at least three of the following:
- Nonconventional student entry requirements or selection processes;
- Increasing integration of work-based learning;
- Blending of off-campus online learning with on-campus intensive experiential learning;
- Establishment of student-led, extracurricular activities in contexts and cultures that are not typically associated with non-curricular experiences; and
- Dual emphasis on engineering design and student self-reflection.
The future of engineering education is “rapid and fundamental change,” according to a recent study commissioned by MIT. Among the anticipated changes: the growing leadership of institutions in Asia and South America and a move toward programs that integrate hands-on, socially-relevant learning throughout the curriculum.
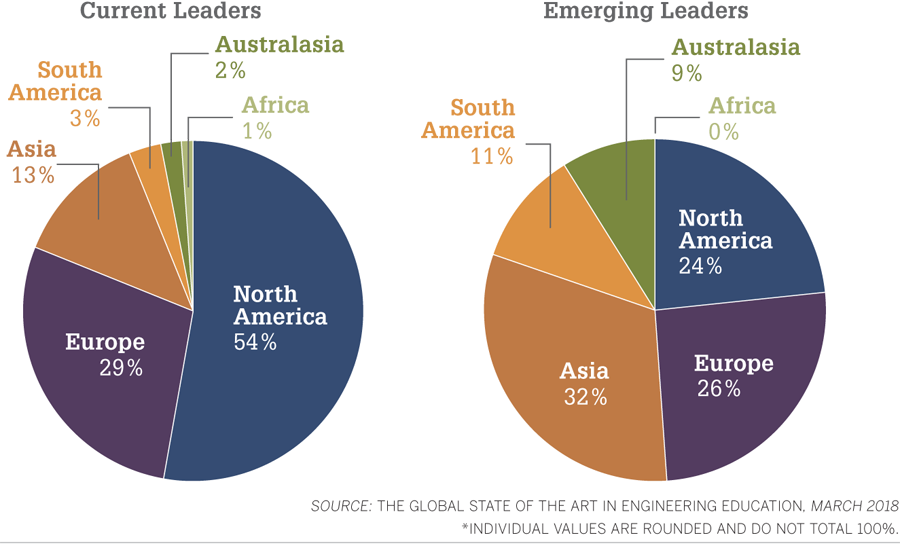
Current leaders in engineering education, the study notes, tend to be US- and European-based research universities. But governments in South America, Asia, and Australia have recognized the potential for strategic investment in engineering education to grow talent and drive economic growth. Thus, the MIT-commissioned report points to an anticipated “tilting of the global axis of engineering education leadership.”
Emerging leaders in engineering education are more likely to be located outside of the US and Europe. Forty-three percent of the emerging leaders identified were located in Asia and South America, while just 16% of the current leaders were located in those areas.
Other characteristics of emerging leaders include multidisciplinary programs and emphasis on both engineering design and student self-reflection.
In addition, emerging leader programs often arose out of systemic educational reform or were developed from scratch. That enables a more “systemic and unified” approach with socially relevant design projects embedded into the program. In contrast, such projects at larger and more established institutions were characterized as “bolt-on activities.”
The report’s emerging leader case studies include institutions where “curricular coherence and integration is delivered through a connective spine of design projects.” For example, at the Singapore University of Technology and Design, multidisciplinary design projects deliver curriculum while contextualizing and integrating learning across courses and years of study.
Most of the thought leaders interviewed for the study felt that “team-based, hands-on student learning that responds to the needs of society and industry” would be the basis of the world’s leading engineering programs in the future. However, thought leaders expressed concern about the ability of big public universities to deliver those experiences to large student bodies and with limited budgets.
As one thought leader said, “The next phase in the evolution of engineering education is for the rest of us to figure out how we can offer this type of quality of education at scale.”
The study predicts the emergence of a new generation of leaders in engineering education where best practices would be delivered through a “coherent and integrated curriculum” that could be provided to large cohort groups under constrained budgets.
The two-phase study examining the global state of the art in undergraduate engineering education was spearheaded by MIT’s New Engineering Education Transformation initiative, which aims to “reimagine and rethink undergraduate engineering education...in a fundamental way across the school.”
Although the study focused on engineering education, the report notes that some of the trends it spotlights will likely play out across university programs. Engineering education therefore has an important role to play: “It has the opportunity to be the catalyst and standard bearer for excellence in higher education, and the incubator from which best practices will develop and spread.”
Access The Global State of the Art in Engineering Education at http://neet.mit.edu.
Leader Locations
Thought leaders designated institutions as current and emerging leaders. The geographic distribution of those schools:


 Volunteering at NSPE is a great opportunity to grow your professional network and connect with other leaders in the field.
Volunteering at NSPE is a great opportunity to grow your professional network and connect with other leaders in the field. The National Society of Professional Engineers (NSPE) encourages you to explore the resources to cast your vote on election day:
The National Society of Professional Engineers (NSPE) encourages you to explore the resources to cast your vote on election day: